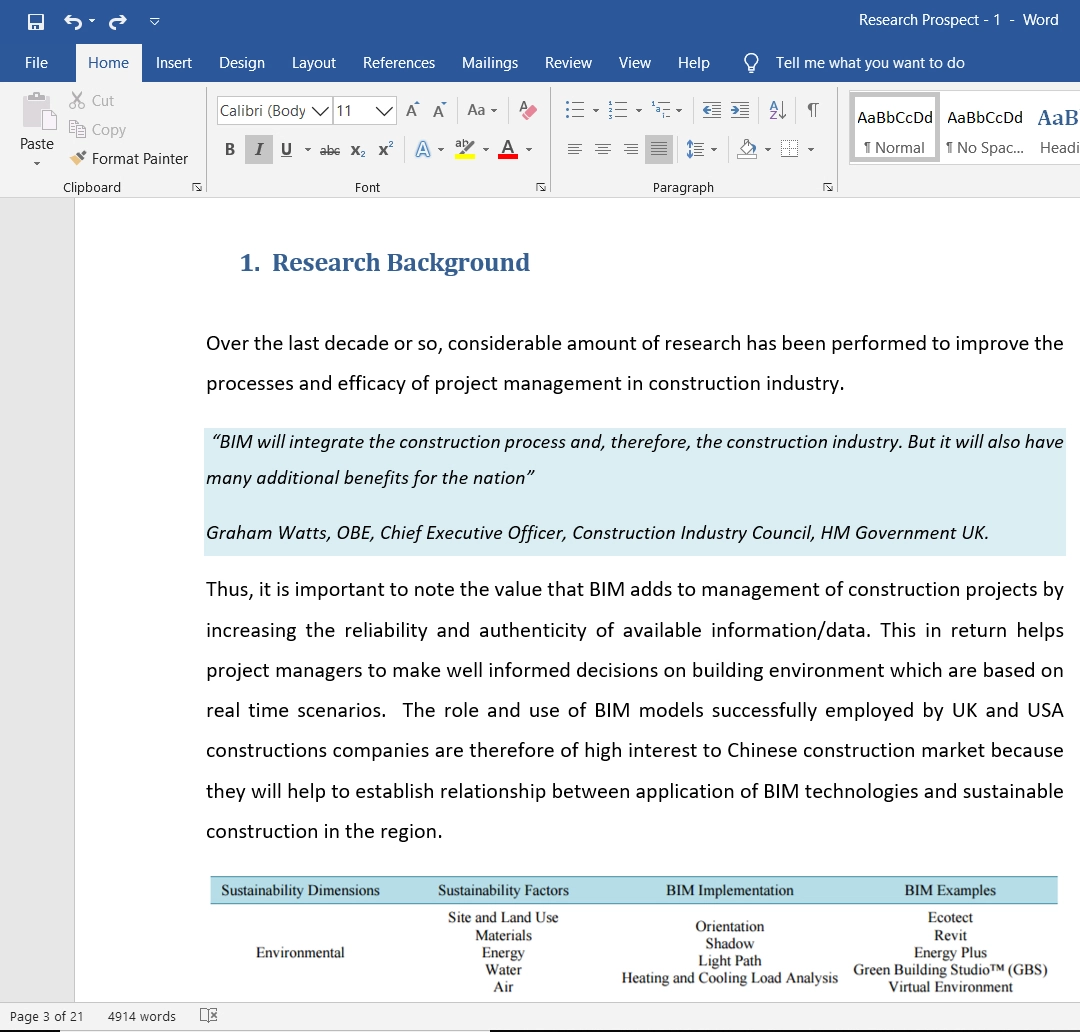
Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness.
The three principal forms of business organization are sole proprietorship, partnership, and corporation. The main differences found among the three are within their ownership structure, the legal status that the business maintains, and the method by which the company’s profits are taxed.
In a sole proprietorship, the business is owned by one single individual. On a note of legality, there is no distinction between the owner and the business. It is considered that the owner is the company and the company is the owner, both being interchangeable and the same. The owner is considered to be personally liable for all of the company’s debts.
Also, all the profits are considered the owner’s income and need to be reported on the owner’s individual income tax return. The advantage of this form of business organization is that it is quite simple. There are no partnership agreements and no corporate formalities that are needed to be performed.
On the other hand, a partnership is a business with two or more owners. Partnerships come in two types; general and limited. Within a general partnership, each partner is personally liable for all of the debts of the business. On the other hand, a limited partnership allows some partners to have limited liability.
This means they are a debt to what they’ve invested into the business and not more than that. Furthermore, partnerships do not pay income taxes and instead report the company’s profits and losses as personal income according to the company’s share.
The advantage of this form of business organization is the distribution of debt and profit. It may also be easier to start up a business as the investment lies in each of the partners.
Lastly, a corporation is considered an individual entity or a “person” for legal matters. It is a separate and distinct entity from its owners and shareholders. The company itself is responsible for debts. However, the shareholders still have a chance of losing money which they have invested but not more.
The corporation directly pays taxes on corporate profits, but only if they are distributed as dividends. An advantage of a corporate organization is limited liability for shareholders and the advantage of raising funds by selling stocks or bonds. However, there is also the disadvantage of greater regulation on both the state and federal levels.
Ross, Westfield, and Jordan. (2008). Forms of business organization. Fundamentals of Corporate Finance. Retrieved from
http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/007353062x/student_view/ebook/chapter1/chbody1/
1_2_forms_of_business_organization.html
A financial intermediary such as a bank simultaneously interacts with savers or lenders and borrowers and produces a set of services that facilitate the transformation of its liabilities, such as deposits into assets, such as loans. The function of facilitating liabilities or assets into assets or liabilities is called intermediation. Through intermediation, financial intermediaries allow indirect lending and borrowing between savers and borrowers.
Financial intermediation can improve economic efficiency in at least five ways by:
• facilitating transactions
• facilitating portfolio creation
• easing household liquidity constraints
• spreading risks over time; and
• reducing the problem of asymmetric information
Chandra, P. (2010). Fundamental Financial Management (4th ed.). New Delhi: McGraw- Hill.
A primary market is considered a market in which corporations raise capital by issuing new securities. Within this market, the firm sells (or floats) new stocks and bonds to the public for the first time. An initial public offering (IPO) is a stock issue in which privately held firms go public. Thus, an IPO is considered an example of a primary market transaction. An IPO can be complicated due to the various rules and regulations that dictate the processes of institutions. It should be noted that in a primary market, the securities are purchased directly from an issuing company.
Investopedia Staff. (2015). A look at primary and secondary markets. Investopedia. Retrieved from http://www.investopedia.com/articles/02/101102.asp.
Orders completed by our expert writers are
The two major exchanges in the United States are the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. They are about the same platform regarding the stock market. Still, their modus operandi differs extensively based on their equities and how they handle the stock market operation when selling and buying stocks.
Firstly, the market type differs, as the NASDAQ established a ‘dealer-based’ securities market, in which dealers sell stocks directly to firms or investors through the telephone or internet. On the other hand, the NYSE established an ‘auction style’ securities market where brokers purchase stock on clients or firms.
Trading locations of both exchanges differ as NASDAQ trading takes place electronically or through the internet, whereas trading on NYSE takes place in person on the exchange floor. NASDAQ has fewer trade restrictions, opening up a market for smaller companies to meet the stock exchange qualifications to trade publicly.
In contrast, NYSE-traded companies possess at least 2200 shareholders, trade 100,000 shares monthly, and possess a $100 million market capitalization with revenues of $75 million annually.
Staff Writer. (2013). Difference between the two largest stock exchanges in the U.S. International Finance Magazine. Retrieved from http://www.internationalfinancemagazine.com/article/Difference-Between-the-Two-Largest-Stock-Exchanges-in-the-US.html.
The firm cannot pay a $20 million cash dividend because the $20 million of retained earnings doesn’t mean the company has $20 million in cash. The retained earnings figure represents the cumulative amount of net income that the firm has not paid out as dividends during its entire history. Therefore, most of the reinvested earnings are more probably spent on the firm’s operating assets.
Operating capital is the money a business needs in over to cover its daily expenses. In an ideal situation, operating capital comes from business activities that bring money. This includes sales and rentals of business property. However, it becomes necessary that the business find a source of operating capital to stay afloat in the market even during periods when the company is not profitable. Operating capital is often defined as the difference between current assets and current liabilities.
It is the capital that is available for firms’ operations, including manufacturing, transportation, production, and more. These are different from financial transactions and long-term improvements. Operating capital is important as it allows the firm to perform its daily activities. In most cases, it is the cash that the firm has in hand to meet its daily functional requirements.
Operating capital is considered a good measurement metric of the short and medium-term financial health of a business. It can indicate how much the company can expand its operations without using borrowing or other capital-raising techniques.
Vijayakumar, A. (2001). Working Capital Management- A Comparative Study. New Delhi: Northern Book Centre.
Net Income: $6,000,000
Tax Rate: 40%
EBT = Net Income/(1-T)
= $6,000,000/(1-.40)
= $10,000,000
EBT =EBIT- Interest Expense
= $13,000,000 – $10,000,000
Interest Expense = $ 3,000,000 (ANSWER)
Net Cash Flow = Net Income + Depreciation
Net Income: $3,100,000
Depreciation: $ 500,000
Therefore,
Net Cash Flow = $3,100,000 + $ 500,000
= $3,600,000 (ANSWER)
Model answers can be valuable feedback, showcasing expected standards. However, personalized feedback that explains errors and encourages critical thinking is often better. It addresses individual needs, aiding deeper understanding and improvement.