Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness.
Cross-cultural human resource management is an organisation’s approach to bring a work culture where employees from different religions, ethnic backgrounds, genders or races can work together. This research aims at understanding the role of cross-cultural HRM in the success of organisations.
The research has collected secondary qualitative data for the analysis of information related to the topic. Considering the data collection method, the research has used the thematic data analysis technique for the interpretation of information. It is found from data analysis that cross-cultural HRM depends on a number of factors, including gender, ethnicity, race, religion etc. With the presence of cross-cultural HRM, organisations are able to maintain positive and motivating work culture, which returns to having success and growth opportunities for businesses.
In the era of globalisation, companies have started expanding their businesses from one location to another. Globalisation has also influenced the movement of people from one country to another. With employees from different cultures and countries, it has become difficult for organisations to manage the employees collaboration.
This has been a major factor that has led to the adaptation of cross-cultural Human resource management or cross-culture HRM concept. Cross-cultural HRM is about the approach used by international organisations for managing their culturally diversified employees. It has become important in contemporary times to adapt cross-cultural management so that the organisational performance can be maintained and the reputation of the business as well.
In an organisational setting, cross-cultural HRM is followed or obligated with a specific number of factors. For example, fostering a strong relationship between employees, embracing diversity, and open communication are the major factors that influence the incorporation of cross-cultural HRM .
A workforce with diversity possesses challenges in terms of region, communication and customs. In such a situation, an organisation not only requires to accept the differences but also the focus should be maintained for having a collaborative approach. Multinational organisations mainly adopt the concept of cross-cultural HRM. Those organisations that try to adapt the concept of cross-cultural HRM mainly focus on having a collaborative work culture.
Cross-cultural HRM has become a trending topic or aspect in the organisational work procedure. One of the major reasons for the surge of cross-cultural HRM in the workplace setting is due to globalisation. Globalisation has forced companies to expand businesses from their home country to other markets.
With such strategies, the presence of employees from different religions, races or ethnicities has been increased. This factor has led to cross-cultural HRM adapting so that a single framework or work approach exists in a business. As cross-cultural HRM has become a trend thus, it is important to explore more information on the topic.
There are very few studies that have focused on exploring cross-cultural HRM. This has been the influencing factor that enforces to conduct of the research on the topic of cross-cultural HRM. Other than this, organisations’ approaches to eliminating the conflict and biases related to diversity have also been the major factor behind doing the research or understanding the impact of cross-cultural HRM. The impact of cross-cultural HRM on the success of an organisation is the most important factor to perform the research; this area has not been explored extensively.
The study aims to analyse the role of cross-cultural HRM in the success of different organisations.
Objectives of the research are as follows:
Research questions are as follows:
Orders completed by our expert writers are
A literature review is the section of research that illustrates the theoretical information related to a research study. This research section has also reviewed the literature by reflecting on the theoretical information. The literature review has been done by considering the objectives of this research.
Based on the objectives, this research focuses on understanding the concept of cross-cultural HRM, the factors to be integrated into the cross-cultural HRM and the significance of cross-cultural HRM for a company’s success. The journal articles published in recent time or the last five years have majorly been focused on while conducting the literature review.
Globalisation has been the influencing factor behind the incorporation of cross-cultural HR management in different organisations. Mainly organisations like multinational companies are influenced to consider cross-cultural HRM for better management of employees.
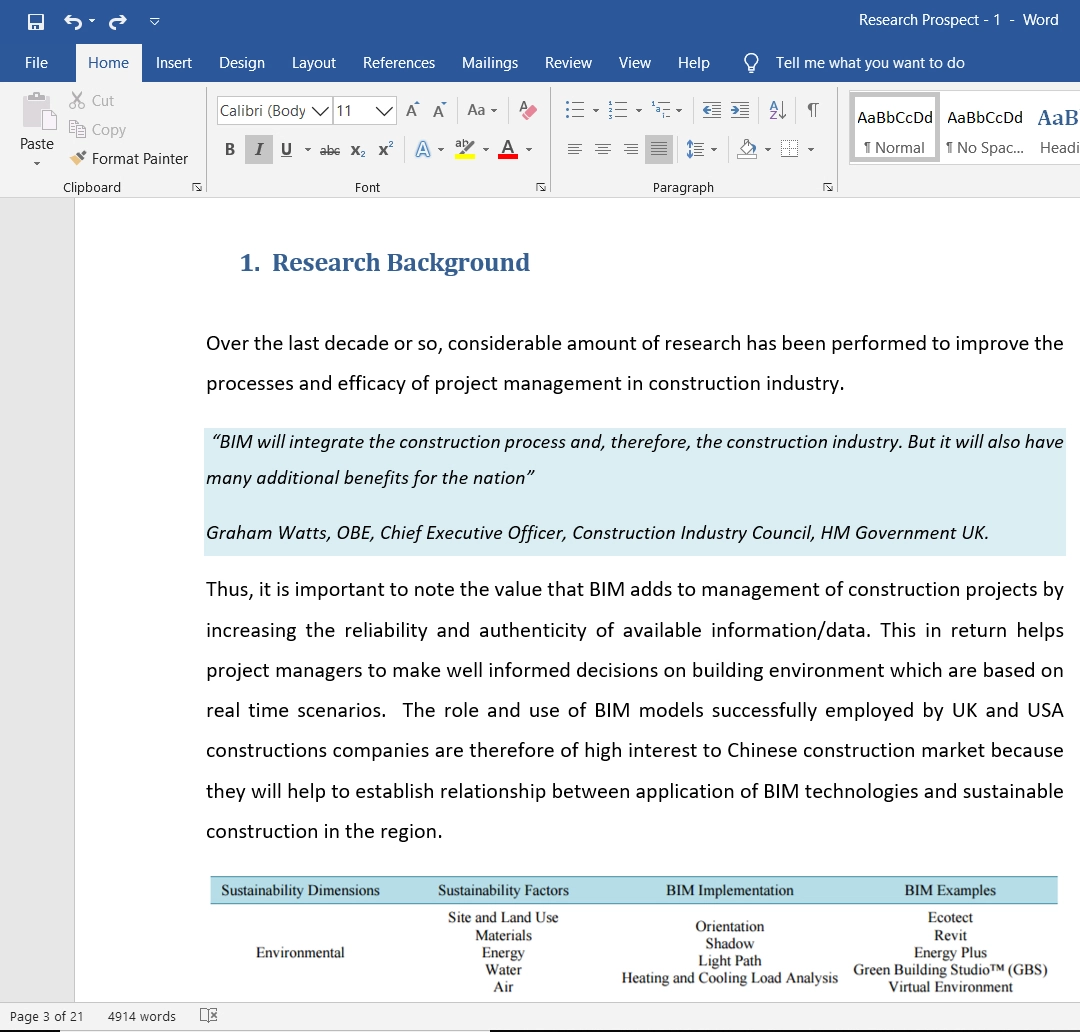
According to Romani, et al. (2018), cross-cultural HRM shows an organisation’s tendency of having a diversified group of employees and the work culture of employees. Cross-cultural HRM is the vital piece of culturally diverse administration in an organisation. It is a succession exercise dependent on characters of cultural contrasts of staff determinations, pay rates, the board, etc.
These factors help improve human resources’ effectiveness and develop a positive cultural environment. The major factors of cross-cultural HRM are related to or based on three major factors. It includes the culture of an organisation’s home country, the business structure and the difference in culture among the employees. The culture of different organisations is normally influenced by the culture of a company’s home country. However, cross-cultural HRM helps maintain a balance and collaborative work culture in such a scenario.
Figure 1: Cross-cultural HRM, Source:
Culturally diverse HRM helps an organisation to bring trust among the employees and results in the firm’s progress. According to Bird and Mendenhall (2016), such results through cross-cultural HRM are important for a company as it increases its foothold in different countries and cultures.
The trust between the employees develops in an organisation with proper interchanges and understandings of thoughts. It is also claimed by the researchers that such understandings and interchanges can only be developed if meeting or collaboration is common in the workplace.
The authors also suggested that the development of trust between the employees helps them feel comfortable in the workplace and consider the workplace an important part of their life. With such intention, the employees also provide extra dedication to work for the betterment of the organisation. On the contrary, Nikitenko, et al. (2017), claimed that the presence of cross-cultural employees could cause conflict due to the difference in values, etiquettes or religious differences.
As per the study of Alam and Rasheduzzaman (2018), incorporating diversity in organisations capability takes time, experience and transparency. By Bird and Mendenhall (2016), the intercultural inabilities or difficulties of employees to fit with the culture of others leads to the issue of miscommunications, and the impact on business relations with the suppliers and other partners.
As a result, the deadline can be missed, activities may come up short, and skilled individuals can go for rivalry. Key HR duties are to see how diverse components interface with HRM, and the course for hierarchical learning for cross-cultural knowledge and encourage cross-cultural correspondence all through the association.
As per the study of Nikitenko, et al. (2017), team building is an ignored aspect of the business world. Building connections or relationships among staff is significant, to keep everybody occupied with the capability of work as well as performing the undertakings effectively.
From a philosophical viewpoint, it can be said that uniting individuals from totally various cultures to pursue a similar objective is the thing that causes people to develop aggression against a specific race. The factors of exploring the important correspondence as well as flawless coordination become important for businesses.
According to Riener and Wiederhold (2016), different labour forces or employees belonging to diverse cultures present difficulties regarding duties as well as in communication. In such circumstances, it is imperative to acknowledge contrasts, and take complete control over the activities of an organisation.
Accepting those distinctions as well as utilising a common vision is essential in making business fruitful. Setting out open doors for representatives to explore their collaborators’ points of view and lifestyles is fundamental to assemble an effective workplace environment and offer staff opportunities for long commitments.
Figure 2: Cross-cultural HRM Factors Source:
In accordance with Zhao and Pan (2017), embracing diversity is a major factor in bringing cross-cultural HRM to an organisation. The authors claimed that an organisation could bring employees from diverse locations, leading to a difference in communication techniques, customs and culture.
In such a situation, this factor becomes important for organisations to not only accept differences but also integrate them and their opinions while taking a crucial business decision. The authors also claim that the success of an organisation depends on the provision of openness of operation to a wide range of cultures.
With the share visions between the employees from different cultures, it becomes easier for organisations to adopt a cross-cultural approach. Nikitenko, et al. (2017) highlighted that the promotion of diversity in the workplace could not be done or brought by a single person; rather, a collaborative effort is required to promote diversity.
In this process, the authors have identified the development and arrangement of the training programme as a key aspect. Such a situation not only brings a cultural approach to diversity but also helps and influences the overall community and brings a holistic culture of work.
It is a fact that the development of a good and work-friendly work culture depends on co-workers’ perspectives. With a better understanding between the employees, it becomes easier for organisations to develop a healthy work culture that leads to improving the quality of work scope of success for a company.
Cross-cultural HRM in an organisation helps in having a positive culture of work between the employees or the entire workforce. According to Nikitenko, et al. (2017), communication is a major aspect of success in an organisation. Having proper and effective communication helps a company to build a strong connection between the employees.
Teamwork or a collaborative approach to work is a major factor behind the success of an organisation. In this regard, the author claimed that communication without problems or barriers could help a business develop a team and avoid complications between workers.
This results in building a team and influences the success of an organisation. Following cross-cultural aspects, HRM in organisations can create a single framework or approach for working. With such an approach, the difference between the employees and the communication gap can be eliminated with a simplified approach.
It is evident in previous studies that multinational organisations are more focused on and aimed at adapting cross-cultural HRM for solving the cultural barrier. Alam and Rasheduzzaman (2018), also claimed that the presence of employees from different cultures enforces organisations to bring a single framework of work in human resources.
Cross-cultural HRM is also important for an organisation to follow the guideline of international HRM. With such an approach, businesses find it easy to create a work-friendly workplace that is obligated to all the ethical factors of work as per international HRM.
It is summarised that cross-cultural HRM is becoming important for organisations to bring a positive work culture. The presence of employees from different regions, cultures and communication gap has been the major factors for bringing cross-cultural HRM.
Multinational firms mostly adopt cross-cultural HRM as they have a major number of employees from a different culture. Adaptation to cross-cultural HRM also helps organisations in growing in the market. This is because the approach influences teamwork and eliminates the gap that exists due to communication or culture.
Research methodology is an integral section of research that directs the way of data collection and analysis in research. Research philosophy, approach, strategy and design are the common parts of a research methodology section. The research methodology has been explained and justified in this chapter of the research. The approach of data collection and analysis has also been explored in this research section. Further, the ethical considerations followed in the research have also been discussed in the study.
Research philosophy is defined as the belief that a researcher considers to research a particular topic. Based on the research philosophy, a researcher progresses to conduct research with a clear perspective. Interpretivism research philosophy, positivism research philosophy and realism research philosophy are the common research philosophy.
In this study, the selected research philosophy is interpretivism research philosophy. The research philosophy is about the interpretation of elements related to a research topic or variables. Considering the research philosophy, the study can be considered for the interpretation of two variables: cross-cultural HRM and an organisation’s success. Although, the research has rejected the positivism research philosophy. This is because the research philosophy is more relevant to the observation process, which can divert this research towards the wrong side.
The research approach is the strategy and plan for data collection and analysis on particular research. Inductive and deductive are the common research approach which is followed in research to collect and analyse data. In consideration of the research topic, it can be said that the selected research approach is based on an inductive research approach.
The research approach starts with an observation, and a theoretical base is given at the end of the research. By considering the research approach, the research has focused on evaluating the variables associated with the research. The research is based on a topic, not a statement that reflects the need to perform observation to develop theory at the end. By obligating to the fact, this research has focused on considering the inductive research approach.
Research design helps research to maintain a systematic and synchronised approach to data collection and analysis. Exploratory, explanatory and descriptive are the common and major research design which is used in research. This research has considered the explanatory research design to conduct the research on the topic.
Explanatory research design is about conducting research on a topic that has not been explored with efficacy, and the problem has not been explored yet. By considering the research design, this study has focused on choosing the explanatory research design. The research design is relevant in the research as the area of cross-cultural HRM has not been explored in previous researches due to the topic’s emergence in recent times.
The research strategy is used to direct research towards a proper data collection process. Qualitative interviews, quantitative survey, case studies, and ethnographic are the common research strategies which are used in research. Based on the research strategy, research progresses to collect data and analyse.
This research considered the ethnographic research strategy to collect data and analyse the information. Based on the topic, the selection of the strategy is effective in performing the research. The research strategy is about explaining a phenomenon as it exists theoretically. With the consideration of the research strategy, the research can collect data and interpret the information as it explains theoretically.
Data Collection is a major part of research that directs research towards data analysis and interpretation. Primary and secondary are the method of data collection which are used in research. Primary data collection involves the direct collection of data from a set of research participants.
In contrast, secondary data collection is about the selection of books, journals and websites for data collection. This research has selected the secondary data collection method to conduct the research. For this purpose, the research has used the sources like books, journals and authentic websites.
During the collection of data, the type of data to be collected is also a major factor in the research. Quantitative and qualitative data are the common types used in research to collect the information. This research has mainly focused on the collection of qualitative data through secondary sources.
Data analysis is a part of research that is decided on the basis of the method of data collection and the type of data collected. This research has collected secondary qualitative data. Thus, the qualitative data analysis technique has mainly been used. Based on the analytical approach to the collected data, this research has conducted the thematic data analysis.
The thematic data analysis is a method of forming themes based on the information of the literature review. The process of forming themes involves topic, code and themes systematically. This research has conducted the thematic data analysis by using the information and selection of the topic from the literature review.
Ethical consideration is mainly required to undertake for the primary data collection as the type of data collection method involves direct interaction. However, this research has followed the ethical consideration for the secondary too. Ethical consideration has been taken by avoiding misinterpreting information as well as the accuracy of the information collected from literature sources. The use of patented articles has also been avoided to maintain ethical consideration in the research.
The key aspect of the research methodology is the selection of data collection and data analysis methods. In this research, the selected data collection method is secondary qualitative data. The selection of data collection methods in the research has been influenced by the research approach, philosophy, strategy, and design.
The selected research philosophy, research approach, research strategy, research design in the research study are interpretivism, inductive, explanatory, and ethnographic, respectively. Based on these aspects, a secondary qualitative data collection method has been chosen, which enforce to use of the thematic data analysis technique. In the research, ethical consideration has also been taken to avoid the legal obligation or other such problems.
This section of the research includes the analysis of data collected through the primary or secondary data collection method. In this research, the collected data collection method is secondary qualitative. Based on the data collection, the research has conducted the thematic data analysis technique. The interpretation of information from the thematic data analysis technique has been given in this section of the research.
| Topic | Code | Theme |
| According to Romani, et al. (2018), cross-cultural HRM shows an organisation’s tendency of having a diversified group of employees and the work culture of employees. | Cross-cultural HRM includes common aspects like diversification and its impact on work culture | Relationship between cross-cultural HRM and diversified work culture |
| In accordance with Bird and Mendenhall (2016), when individuals need intercultural abilities, miscommunications can harm business relations, the deadline can be missed, and activities may come up short, as well as skilled individuals can go for rivalry. | Internal operations and execution of tasks becomes difficult with cross-cultural HRM | Problems and impact of the diversified or cross-cultural group of employees on the organisation |
| According to Riener and Wiederhold (2016), different labour forces or employees belonging to diverse cultures present difficulties regarding duties as well as in communication. In such circumstances, it is imperative to acknowledge contrasts and take complete control over the activities of an organisation. | The problem of communication and inability to control the workforces enforces organisations to adopt the cross-cultural approach | Importance of cross-cultural HRM |
Cross-cultural HRM is developing a workforce whereby employees from different cultures are hired, recruited, and retained. A cross-cultural HRM is the management process where the HR implements cultural diversity within the organisation leading to a diversified workforce of employees.
A cross-cultural HRM is only possible in international organisations, because employees are hired from different communities and cultures, and the organisations have to follow a diverse workplace culture. An organisation operating globally have to hire employees and expatriates from the host country, and as per the organisational culture theories, each community or country has a different culture.
This is when the cross-cultural HRM is needed so that a mutualistic and developmental culture is implemented whereby all members from different communities can work together is cohesion and collaboration following the organisational objectives and governance policies.
Cross-cultural HRM has the roles and responsibilities to understand and assess all the cultures that fit the organisational objectives, and based on these aspects. They can plan the type of employees they want or the formation of a diverse workforce. Therefore, there is a strong relationship between cross-cultural HRM and diverse work cultures.
A cross-cultural HRM comprises of HR employees from different communities, cultures, and regions. This helps the HRM formulate a common cultural system that neither affects the organisational goals nor the sentiments of any culture. As a result, they can formulate a diverse workforce and culture that all the employees and expatriates can follow and improve the organisational climate.
Interestingly, the work culture can be different at different places of operation, like a global company operating in the Asian region will have a different work culture than when the company is operating in the European region and others. Therefore, a cross-cultural HRM has a significant role in forming diversified work culture as they enable the formation of a multicultural organisational climate with diverse linguistics, different ethnicities, genders, and communities.
Based on the findings from the literature review, there are multiple challenges to the formation of a diversified or cross-cultural group of employees. The most important challenges are miscommunication and lack of understanding. Miscommunication can lead to many issues like provision of wrongful or half information, conflicts between employees and managers and also affect the performance of the organisation.
In a diversified or cross-cultural group of employees, they have many languages whereby some may be able to speak in proper English and others may not. As a result, there may be a difficulty in understanding which often leads to miscommunication, and in such cases, it may impact the cohesion between the employees.
However, HRM sorts out ways to tackle these situations like training in local languages or improvement of the English language amongst the employees. Another challenge is that of motivational factors, whereby some employees are motivated when leaders are autocratic and in some cases, the employees are motivated when the leaders are democratic and so on.
The motivational strategies of HRM also vary from one employee to another, like some employees from different cultures are motivated by the workplace environment whereas others are motivated by workplace engagement. Not all strategies are the same in the case of the cross-cultural group of employees, so it is a challenge for HRM to form a cross-cultural group of employees.
The employees’ ethnicity and beliefs vary from culture to culture, and therefore, they have different ways of working or making decisions. Therefore, they may act as challenges for working in a team or team members whereby different people have different ways of working.
Furthermore, in the case of a remotely working cross-cultural group of employees, there are many challenges. One of them is time zone, technical challenges that affect the communication and, in many cases, reduces the efficiency of working.
Analysis of the secondary qualitative data has reflected on the fact that cross-cultural HRM is an organisational approach where the focus is given to developing a team of diversified work culture and workforce. Workforce diversity is the major aspect of bringing cross-cultural HRM to an organisation.
Workforce diversity means the presence of employees from various ranges, genders, ethnic groups. In the process of adopting cross-cultural HRM, human resource management plays the most important role in developing the culture. Such culture is developed if an organisation does not consider any specific age group, gender, or ethnic group to recruit employees.
Along with this, another major factor of developing cross-cultural HRM is the provision of training to the employees for having cross-cultural HRM. With the consideration of cross-cultural HRM, an organisation can able to bring a collaborative work culture and helps in building a cohesive group.
For instance, an organisation with the proper balance of experienced and new employees helps in having well-maintained productivity. This is because a firm with such an approach can help the new employees to learn from the experienced and old staff. While the rate of low productivity among the old employees becomes neutralise with the support and intention of work from the newly joined workforces. The reason for the workability of new employees is their passion and focus on a performance-driven approach to work.
On the other hand, the balance between the male and female workforces helps in having a good work culture. For example, male employees are more prone to show aggression and authoritative work culture. On the other hand, female employees adapt to work culture and show their patience.
Such characteristics of male and female employees influence an organisation to maintain a balance in work approach and perform tasks of different varieties. The gender gap or the glass ceiling concept has also been identified as a major factor behind the importance of cross-cultural HRM in an organisation.
Although, the companies are focusing on bringing balance between the male and female employees. However, the internal environment of businesses leads the female workforce to face complications. It is found that cross-cultural HRM is important to avoid the issues faced by female employees during work.
This is because adapting to cross-cultural HRM helps in having a strong framework to monitor the employees and take necessary steps. Not only have this, but the increasing number of racism attacks or controversies related to race also been the factor or importance of cross cultural human resource management.
The chapter has discussed the analysed data collected from secondary qualitative sources. The analysis shows that cross-cultural HRM is about having a unified and collaborative work culture. With the integration of cross-cultural HRM, an organisation can deliver a message to the competitors and gain a reputation. HRM plays the most important role in adapting cross-cultural HRM. With the presence of cross-cultural HRM, a balanced work culture or approach in the organisation also becomes easy to maintain.
It is concluded that cross-cultural HRM has become important for organisations of the modern era. Globalisation has influenced companies to adopt a work culture where diversity exists. The main reason for such an approach relies on the presence of employees from different cultures and other factors like gender, age, ethnic group.
In the modern era, multinational companies have been expanding to a wide range of areas, and such factors are enforcing them to adopt cross-cultural HRM. In the process of implementing cross-cultural HRM, the HRM plays the main role of designing. With the presence of a proper cross-cultural HRM approach, it becomes easier for companies to grow in the market. This is because the approach helps to have a strong presence and improve reputation. With cross-cultural HRM, organisations are able to maintain a single and common framework that each and every employee can use.
Further, the organisations gain the benefit of cross-cultural HRM with a balanced base of the workforce. Such workforces include young as well as experienced employees and male, female staff. This is a major factor of having a good approach to work and support towards the employees. Businesses can able to bring a culture of learning, motivation, and creativity for the development of business and growth.
In order to manage cross-cultural HRM with effectiveness, organisations are required to focus on a number of areas. For example, consideration of transgender staff or employees from the LGBTQ community is not effective or considerable for many businesses. Organisations should focus on the areas to consider the community and their people for employment. The companies should also consider atheistic people or persons not interested in expressing their religious views for recruitment. Another factor that the businesses must consider is the focus on eliminating specific age for retirement. Rather than this, businesses must focus on giving no limit of time and consider the health of staff to retire. It would help the businesses in having an internal development option for the new employees and solve the critical issues regarding particular tasks.
This study has been conducted on the basis of the secondary data collection method. The reason for conducting the research with a secondary data collection method is the Covid-19 pandemic which restricted the collection of primary data. Along with this, time has also been a major constraint of doing the research with primary data collection. Concerning the issue, it can be said that the research can be conducted with a primary data collection method or on the basis of a specific company in the near future. It would help in understanding and analysing the company’s cross-cultural HRM situation.
Alam, J, and M Rasheduzzaman. 2018. “Cross-Cultural Project on Human Resource Management: An Overview.” International Journal of Science and Business 2 (2): 101-1114.
Bird, A, and M.E Mendenhall. 2016. “From cross-cultural management to global leadership: Evolution and adaptation.” Journal of World Business 51 (1): 115-126.
Brewster, C, E Houldsworth, P Sparrow, and G Vernon. 2016. International human resource management. 01. London: Kogan Page Publishers.
Clarke, V, V Braun, and N Hayfield. 2015. “Thematic analysis.” Qualitative psychology: A practical guide to research methods 1 (1): 222-248.
Kumar, R. 2019. Research methodology: A step-by-step guide for beginners. 01. London: Sage Publications Limited.
Mahajan, H.K. 2018. “Qualitative research methodology in social sciences and related subjects.” Journal of Economic Development, Environment and People 7 (1): 23-48.
Nikitenko, G.V, O.S Zvyagintseva, E.G Sergienko, O.N Babkina, and L.I Chernikova. 2017. “Development of human resources of the organisation with the help of team-building model.” Calitatea 18 (157): 132.
Reiche, B.S, G.K Stahl, M.E Mendenhall, and G.R. eds. Oddou. 2016. Readings and cases in international human resource management. 01. London: Taylor & Francis.
Riener, G, and S Wiederhold. 2016. “Team building and hidden costs of control.” Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization 123 (1): 1-18.
Romani, L, C Barmeyer, H Primecz, and K Pilhofer. 2018. “Cross-cultural management studies: state of the field in the four research paradigms.” International Studies of Management & Organization 48 (3): 247-263.
Snyder, H. 2019. “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines.” Journal of Business Research 104 (1): 333-339.
Zangirolami-Raimundo, J, J.D.O Echeimberg, and C Leone. 2018. “Research methodology topics: Cross-sectional studies.” Journal of Human Growth and Development 28 (3): 356-360.
Zhao, B, and Y Pan. 2017. “Cross-cultural employee motivation in international companies.” Journal of Human Resource and Sustainability Studies 5 (4): 215-222.
The time to write an undergraduate full dissertation varies, but it typically takes several months, including research, drafting, and revisions.