Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness.
Social media evolution has led to new methods of seeking and getting information on various products and services in the market (Voramontri and Klieb, 2019). Social media has been one of the most significant ways of finding how consumers tend to behave (Chu and Kim, 2011).
Moreover, as mentioned by Xhema (2019), the evolution of social proof has resulted as a greater force for affecting consumers’ buying decisions. It has identified as the tendency to which people imitate the behaviour of others by word-of-mouth and the reviews on their desired products.
However, it is crucial with respect to the instant reach to a number of consumers active on social media as brands target audience via effective strategies of creative content and visuals, discounts, promotions, and influencers. In the words of Fotis (2015), the behaviour of buying today is modified via online decision making which is characterised by information overload as modern consumers today are bombarded with thousands of pieces of information each day.
The typical consumer’s evaluation is significantly reliant on how marketers implement the communication strategies used on social media initiated by need recognition (Voramontri and Klieb, 2019). Moreover, modern-day consumers are increasingly influenced by online tools such as blogs, YouTube and Facebook therefore with the accessibility and availability of the word of mouth via electronic mediums the wide coverage of information allow consumers to identify the various opinions about services and products they consume (Fotis, 2015).
This research illustrates the implications of social media on consumer’s behaviours. In this study, the areas covered are the aims and objectives of the study, the relevant literature regarding the information provided, and the methodology.
As stated by Fotis (2015), considering that consumers day-by-day are becoming a part of not only buying process but also the distribution and design, today it has become a challenge to develop services and products that align with the needs of consumers.
Moreover, the changing demands of consumers required innovation in marketing with respect to meeting the differentiated needs of consumers based on their culture and lifestyles. The research by Chivandi, Samuel and Muchie (2019) elucidated that usage of social media networks has effectively established two-way communication among firms and individuals.
The interactive nature of digital marketing via social media has impacted consumer engagement however this is modified by the online presence. The research although has explained the ways in which social networks are utilised for consumer interaction.
However, a gap identified with respect to the various factors that influence consumers’ buying behaviour. The current study will be carried out by addressing the identified gap with respect to factors pertinent to social media which have a potential influence on consumers by conducting surveys from social media marketers of different firms. This will be effective for examining how organisations modify their strategies of social media advertisement to capture a large target market.
Orders completed by our expert writers are
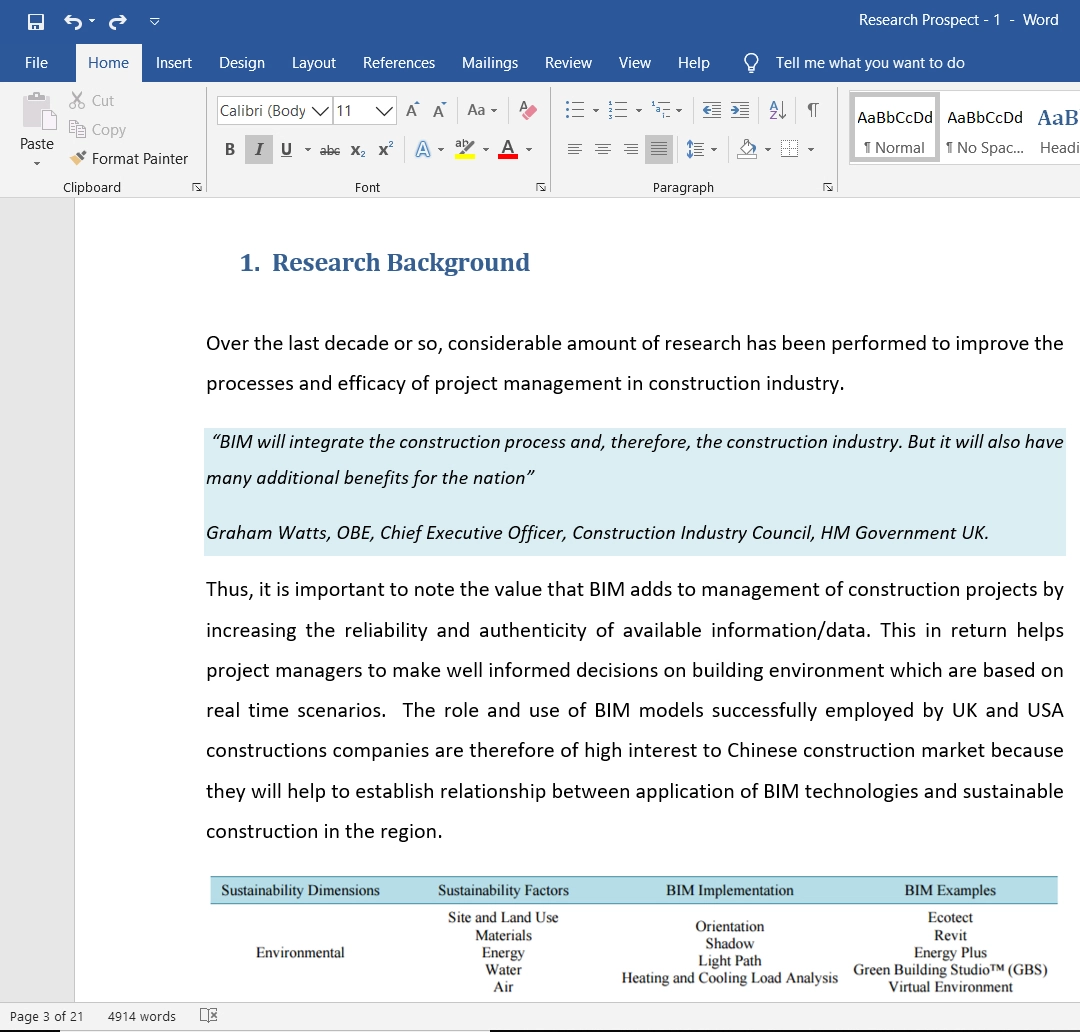
The current research will address the identified gap in the literature by collecting real-time data regarding how marketers modify their social media strategies via survey questionnaires. For this purpose, the researcher by the collection and analysis of numerical data will be identifying the relationship between the different factors of social media and buying behaviour of consumers by the application of regression and correlation analysis. The mentioned aim and objectives in the section will be critical analysed in detail in the research with suitable methodologies.
The study aims to understand the impact of social media on consumer behaviour patterns with regards to goods and services. The objectives of the study are as follows:
How the various factors of social media create an impact on consumer behaviour patterns with regards to goods and services?
The famous theory by McLuhan presented his theory based on the quote “the media is the message”. The philosopher argued that the actual content of media transforms society and people which are pertinent to communicating the frequency and interactivity of new communication patterns which modified consumer behaviour (Young, 2019). The impact of media on society is greater due to the increased participation and effort exerted by the viewers. Therefore, the theory can be effectively utilised for transforming social media for users by the content it contains varied by the mode of effective communication it entails (Pan and Crotts, 2012). For instance, the micro-blogging service Twitter only has a limitation of 140 characters which has made Twitter a more real-time app for sharing information. As business consumers and managers, there is a need to realise the changing customer behaviour by the adoption of an attitude of acceptance via the use of a social media landscape at the cost of innovation (Pan and Crotts, 2012).
As Pan and Crotts (2012) analysed, a sociological and psychological theory that is useful for the interaction of two parties by using a cost-benefit analysis framework is known as social exchange theory. The theory is pertinent to explaining how human beings communicate with each other to form relationships and bonds that are vital for bonding.
It is related to the many times mutual reinforcement could be analysed through rewards such as prestige, opportunity, conformity and acceptance (Cropanzano et al., 2017). In the context of social media and consumer behaviour, the relevance of the social exchange theory is associated with the social media sites and blogs that by far are known for creating the people consuming information rather than generating it.
It is linked with the watchers, sharers, commenters and producers responsible for creating content to express their recognition and identity (Ahmed et al., 2018). However, framed in social exchange theory, watchers do not reciprocate from the exchange suggesting that they consider the cost of commenting is too high.
Firms attempting to leverage social media to their advantage tend to engage consumers in all four levels of segmentation as waters engage consumers by developing content whereas sharers simplify the process of forwarding content via links or reposts (Pan and Crotts, 2012).
According to Di Gangi and Wasko (2016), the interaction model between user and organisation is focused on the social media interactions supported by the platforms of social media provided by an organisation. It was originally built as per the concept of user engagement within the context of the interaction between a user and organisation outlining the distinctions of individual factors of user engagement, user experiences and usage (Dolan et al., 2019).
Therefore, in the context of this research social media engagement theory is pertinent to the rise in social media platforms to create a unique shopping experience for a user from direct participation to content stemming. Besides, Di Gangi and Wasko (2016) mentioned that the social engagement theory is also associated with technical features, including the extent to which users retrieve information and interact with each other. In addition, it is also linked with the flexibility of use features for multiple purposes providing an ability to integrate content to meet the specific needs of consumers.
The advent of social media networking platforms has become the latest phenomenon in the present society by connecting people in one click, irrespective of where people are residing (Sharma, 2014). The technological aspect has changed how consumers engage in shopping as the traditional ways of shopping have been left behind due to the initiation of online shopping (Blázquez, 2014).
According to Nash (2019) and Wang (2017), consumer behaviour is related to the study of pupils, groups and/or organisations and the procedures of their selections of the goods and services; along with the effect of these procedures onto societies and consumers.
Moreover, the study of Darley et al. (2010) stated that marketing experts of organisation do take into consideration of how important is the use of social media in the area of consumers decision making. On the other hand, the study by Xhema (2019) has shown that there is a direct and negative association between customer tolerance and social media such that consumers who spend more time on social media to make their buying decision are less tolerant to overpricing and bad service.
On the contrary, the relationship between social media usage and consumer experimenting is positive. With the increase in social media usage consumers are more willing to try new products without seeing them physically. The study by Fotis (2015) examined the relationship between brand awareness and social media platforms.
It depicted that the effective use of social media platforms varies with respect to the marketing strategy tools in business performance. The results revealed that social media has a direct influence on the online selling point with respect to the consumer loyalty of millennial.
However, most of the benefits of social media are linked with how frequently businesses are engaging consumers for brand awareness. As mentioned by Chivandi, Samuel and Muchie (2019), an adequate manner of assessing the consumer choices before, during and after the purchase are related to a special type of social media such as rating websites and consumer reviews which affects the process of decision making of consumers by information search.
The research addressed that social media-related search can be modified by affecting the set of behaviours and cognitive functions which may include communication, decision making, self-expression, inspiration and collaboration of the brands with consumers.
As mentioned by Žukauskas, Vveinhardt and Andriukaitienė (2018), a belief related to gathering and analysing data is termed as research philosophy, categorised into pragmatism, positivism, and interpretivism. The research philosophy used for this study is positivism, which claims that the social world can be understood objectively.
Moreover, as mentioned by Alakwe (2017), the approach that relied on scientific evidence such as statistics and experiments is positivism as it is useful for revealing the true nature of society. The reason for using positivism research philosophy will help in attaining a broader view regarding the comprehension of social media impact on consumer behaviour, through the use of statistics and measuring results.
The research approach is categorised into inductive and deductive methods of reasoning selected based on the nature of the study. In the current study, the deductive reasoning approach will be used as it allows the scientific investigation of existing theories and phenomena aimed at testing the hypotheses that emerged from existing theories.
Furthermore, according to Stephens et al. (2020), the deductive approach of reasoning is beneficial for determining the causal relationships between variables and concepts which is also vital for the generalizability of results to a certain possible extent.
The research methods are categorised into qualitative and quantitative approaches. As stated by Aspers and Corte (2019), qualitative research is associated with text-based data which is pertinent to the analysis of more in-depth results. On the other hand, quantitative research is linked with numeric data which presented causal relationships between variables with a huge amount of data.
The researcher will carry out quantifiable observations to help attain statistical analyses. It was selected to examine the association between factors pertinent to social media and consumer behaviour as according to Goertzen (2017), the quantitative method allows analysis of results in a broader context with objectivity and high accuracy with the inclusion of close-ended information. It is known that the possibility of bias is very low in this method and the analysis of data is relatively easy.
In the current research, participants will be sampled using non-probability sampling in which the researcher selects the study participants via subjective judgement. Therefore, to select the respondents heavily on the basis of expertise, the purposive sampling technique, a category of non-probability sampling, will be utilised to select the experts in the field. For this purpose, 100 marketers as well as consumers will be selected via purposive sampling to fill up the survey questionnaire.
The collection of primary data is carried out via first-hand sources such as interviews and surveys, etc., however, the secondary data is collected from existing sources such as journal articles, books, etc. (Johnston, 2017). In the current research, primary data will be collected via survey questionnaires whereas secondary data collection will be used for the purpose of the literature review.
For the purpose of this study, the quantitative research method will be selected as it will enable the author of this study to approach a large scale of participants by commencing the distribution of survey questionnaires. A filed research will be conducted in this research for the collection of primary data by examining the participants’ views through the conduct of surveys.
The data analysis will be carried out in the form of correlation and regression analysis by the use of SPSS which is statistical software that allows the determination of associations between independent and dependent variables of the study.
The research study will abide by all the ethical norms to ensure that the study remains ethically viable and is considered reliable and valid. One ethical norm that the research will ensure is to keep the data of the participants confidential to maintain their privacy (Chu and Ke, 2017; Thanem and Knights, 2019). To assure confidentiality and data integrity, the selected participants of the study will be asked to fill in an informed consent before conducting surveys.
Ahmed, A., Khuwaja, F.M., Brohi, N.A., Othman, I. and Bin, L., 2018. Organizational factors and organizational performance: A resource-based view and social exchange theory viewpoint. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 8(3), pp.579-599.
Alakwe, K.O., 2017. Positivism and knowledge inquiry: From scientific method to media and communication research. Specialty Journal of Humanities and Cultural Science, 2(3), pp.38-46.
Aspers, P. and Corte, U., 2019. What is qualitative in qualitative research. Qualitative sociology, 42(2), pp.139-160.
Blázquez, M., 2014. Fashion shopping in multichannel retail: The role of technology in enhancing the customer experience. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 18(4), pp.97-116.
Chivandi, A., Samuel, M.O. and Muchie, M., 2019. Social Media, Consumer Behavior, and Service Marketing. In Consumer Behavior and Marketing. IntechOpen.
Chu, H. and Ke, Q., 2017. Research methods: What’s in the name?. Library & Information Science Research, 39(4), pp.284-294.
Chu, S.C. and Kim, Y., 2011. Determinants of consumer engagement in electronic word-of-mouth (eWOM) in social networking sites. International journal of Advertising, 30(1), pp.47-75.
Cropanzano, R., Anthony, E.L., Daniels, S.R. and Hall, A.V., 2017. Social exchange theory: A critical review with theoretical remedies. Academy of Management Annals, 11(1), pp.479-516.
Darley, W.K., Blankson, C. and Luethge, D.J., 2010. Toward an integrated framework for online consumer behavior and decision making process: A review. Psychology & marketing, 27(2), pp.94-116.
Di Gangi, P.M. and Wasko, M.M., 2016. Social media engagement theory: Exploring the influence of user engagement on social media usage. Journal of Organizational and End User Computing (JOEUC), 28(2), pp.53-73.
Dolan, R., Conduit, J., Frethey-Bentham, C., Fahy, J. and Goodman, S., 2019. Social media engagement behavior: a framework for engaging customers through social media content. European Journal of Marketing.
Fotis, J.N., 2015. The Use of social media and its impacts on consumer behaviour: the context of holiday travel (Doctoral dissertation, Bournemouth University).
Goertzen, M.J., 2017. Introduction to quantitative research and data. Library Technology Reports, 53(4), pp.12-18.
Johnston, M.P., 2017. Secondary data analysis: A method of which the time has come. Qualitative and quantitative methods in libraries, 3(3), pp.619-626.
Nash, J., 2019. Exploring how social media platforms influence fashion consumer decisions in the UK retail sector. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management: An International Journal.
Pan, B. and Crotts, J.C., 2012. Theoretical models of social media, marketing implications, and future research directions. Social media in travel, Tourism and hospitality: Theory, practice and cases, 1, pp.73-86.
Sharma, S., 2014. Social Networking Sites as a Marketing Communication Tool: Opportunities and Challenges (Doctoral dissertation, Aligarh Muslim University).
Stephens, R.G., Dunn, J.C., Hayes, B.K. and Kalish, M.L., 2020. A test of two processes: The effect of training on deductive and inductive reasoning. Cognition, 199, p.104223.
Thanem, T. and Knights, D., 2019. Embodied research methods. Sage.
Voramontri, D. and Klieb, L., 2019. Impact of social media on consumer behaviour. International Journal of Information and Decision Sciences, 11(3), pp.209-233.
Wang, T., 2017. Social identity dimensions and consumer behavior in social media. Asia Pacific Management Review, 22(1), pp.45-51.
Xhema, J., 2019. Effect of Social Networks on Consumer Behaviour: Complex Buying. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 52(25), pp.504-508.
Young, L.C., 2019. The McLuhan-Innis field: in search of media theory. Canadian Journal of Communication, 44(4), pp.527-544.References
Žukauskas, P., Vveinhardt, J. and Andriukaitienė, R., 2018. Philosophy and paradigm of scientific research. Management Culture and Corporate Social Responsibility, 121.
To write the literature review chapter of a dissertation: