Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness.
“The Synergy Between Entrepreneurship and Technological Innovation and Its Role in Organisational Development – A Case of Small Business Knowledge Creation”
According to Corporate Finance Institute (2020), SMART objectives can be defined as a pathway to a direction in which a business or an individual aims for and provides the business or an individual with an increased motivation and focus to achieve the objectives or goals that have been set.
SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Timely, which incorporates all important elements or factors to ensure that the developed objectives can be achieved, and the organization focuses and puts great effort in achieving the goals (Bjerke and Renger, 2017). Furthermore, Ogbeiwi (2017) explains SMART goals as:
Therefore, about the research area, it can be noted that the objectives that would be developed will follow SMART criteria so that during the research process the overall aim and objectives of the research are fulfilled. Relevant results are generated which are under the goals.
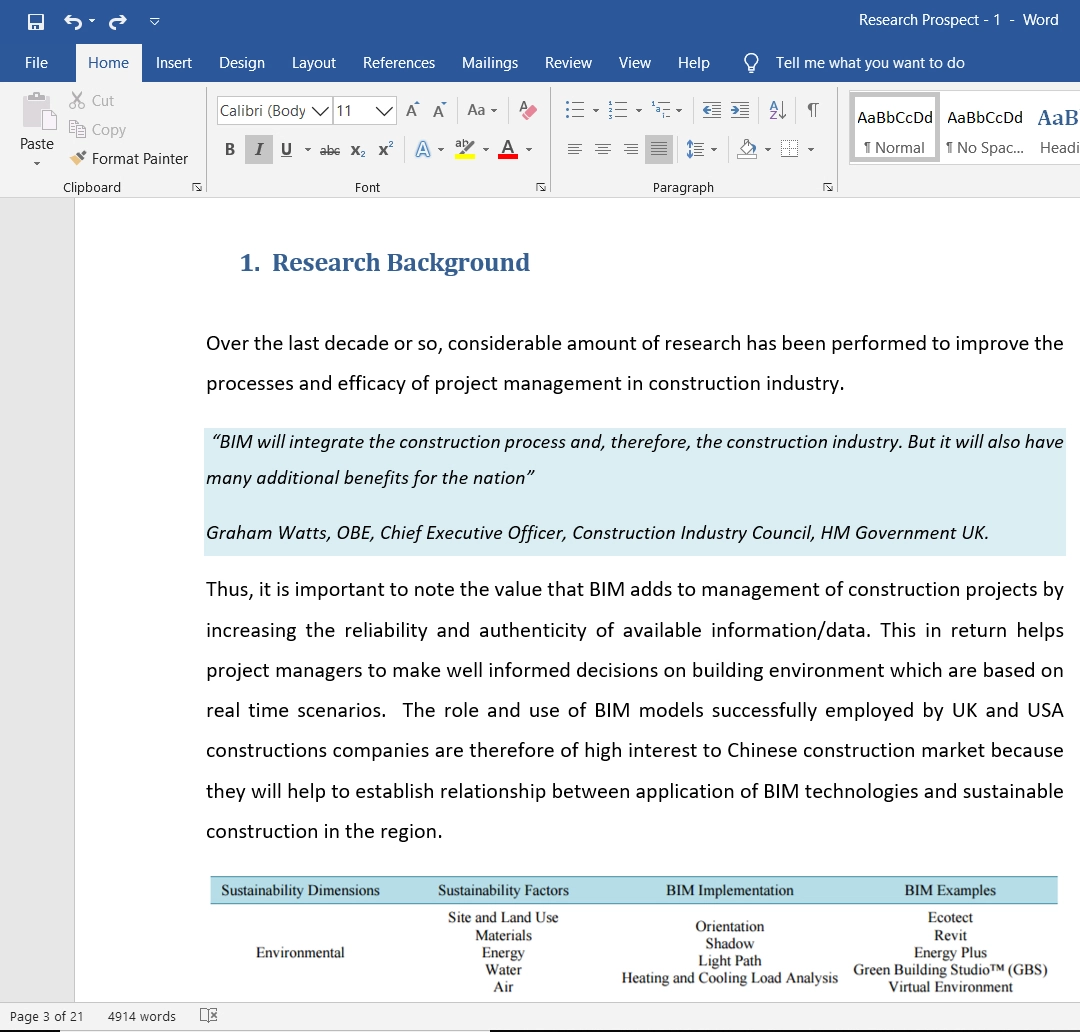
Figure 1: Gantt Chart for the Research Project. Source: Self-made
According to the study of Jeon (2017), the author depicts that the amalgamation of both entrepreneurship and technological innovation is one of the key factors that facilitate the development of an organization in this era of rapid change and technological advancements.
As such, entrepreneurship can be understood as the involvement or development of new ideas and converting these ideas into products which would benefit both the company and the customer (Feki and Mnif, 2016). On the other hand, technological innovations have been closely linked with research and development for more than half a century.
One of the forms of innovation is the invention of new technological products (Shin, Cho and Park, 2018). However, Mohd Noor and Aljanabi (2016) elucidates that innovation does not necessarily have to be invention and it does not have to be technical as well. Hence, throughout academic research and development, ample literature can be obtained regarding the relationship between entrepreneurship and technological innovation and its role in the development of an organization. According to Zhang, Gao and Sun (2018), Sundbo in 1998 summarised three competing paradigms that can be employed to comprehend the relationship between entrepreneurship and technological innovation. These paradigms are as follows:
Orders completed by our expert writers are
This research aims to determine the synergy between entrepreneurship and technological innovation and its role in developing an organization within the case of small businesses knowledge creation. The objectives of this investigation are as follows:
Following are the research questions that this exploration will aim to answer:
Furthermore, in this exploration, the main argument that is to be measure relates to small businesses knowledge creation along with the relationship between entrepreneurship and technological innovation and its role in organizational development. Following is the overall summary of the dissertation:
The sample article that was selected for this study is “Organizational innovation, technological innovation, and export performance: The effects of innovation radicalness and extensiveness” written by authors “Goudarz Azar” and “Francesco Ciabuschi” in 2017 and was published in International Business Review and can be found within the database of Elsevier (URL:<https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0969593116301147>). The structure of the sample articles is as follows (Azar and Ciabuschi, 2017):
| Topic | Author’s Name | Journal Name | Abstract |
|
Azar, G. and Ciabuschi, F., 2017. | International Business Review, 26(2), pp.324-336 | This study focuses on the relevance of different types of innovation for firms’ export performance. Despite ample research on the innovation–performance relationship, previous studies have mainly focused on technological innovations, leaving the effects of organizational innovations relatively unexplored. Hypotheses on the relationship between organizational and technological innovations and firm export performance are tested by structural equation modelling using data from 218 Swedish export ventures. The results indicate that organizational innovation enhances export performance directly and indirectly by sustaining technological innovation. Moreover, by fine-graining our analysis of the mediating role of technological innovation, according to its radicalness and extensiveness, for organizational innovation, we show how the latter enhances both the radicalness and extensiveness of technological innovation. However, notably, the only extensiveness is beneficial for export performance. |
|
Wang, D.S., 2019. | International Journal of Innovation Science. | In developing countries, numerous small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) must innovate because of their scarce resources. This study aims to address the ambidextrous innovation (radical and incremental) associated with firm performance on the SMEs and investigate the moderating effect of environmental factors on the relationship between technological innovation and firm performance. |
|
Feki, C. and Mnif, S., 2016. | Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 7(4), pp.984-999. | This article aims to develop elements of answers to the effect of adequate entrepreneurial activity that would have effects on economic growth. This work analyzes the relationship between entrepreneurship and economic growth for a panel of developing countries over the 2004–2011 periods. In this study, we used two measures of entrepreneurship: the new density and the potential of innovation. We estimated a growth function using static and dynamic panel data. Our results show that the new density and growth are significantly and positively correlated. Our results also show that if the short-term impact of technological innovation on growth is negative, this effect is positive in the long term. This result confirms the theoretical predictions, namely the theory of spillage. |
|
Jeon, I.O., 2017 | Journal of Business Venturing and Entrepreneurship, 12(3), pp.87-105. | This study investigates the effect of entrepreneurship on corporate performance highlighting the mediating role of technological innovation and the moderating role of marketing competence. By identifying the role of technological innovation and marketing competence within the relationship between the entrepreneurship and corporate’s business performance, this study aims to improve SMBs’ competence. Special attention was given to the fact that while some technology-based SMBs have achieved positive outcomes through innovation, some other firms have not been able to deliver expected outcomes despite their technological competence. The data used in this study came from CEO or chief research executives of SMBs. Results of the data analysis show that the innovative sprit, an important factor of entrepreneurship, has a positive effect on technological performance, financial performance and non-financial performance. However, risk- taking tendency has a positive effect on technological performance but negative effects on firms’ financial and non- financial performance. This study also has examined the mediating effect of technological innovation on the relationship between entrepreneurship and corporate performance. The result reveals that technological innovation plays a mediating role within the relationship. |
|
Shin, J.H., Cho, K.T. and Park, S.H., 2018. | Journal of Business Venturing and Entrepreneurship, 13(1), pp.73-87. | Creativity, entrepreneurship, and technological innovation orientation are key factors for technological innovation. The enterprise’s main driver of technological innovation is the firm’s executives. According to the Upper Echelons Theory of D.C. Hambrick(2007), the creativity of the managerial individual will be put into various aspects within the organization’s innovation system. The organizational innovation system is positively influenced by the creativity of the executives, and is achieved by manifesting innovation orientation and technological innovation orientation with innovative performances. The purpose of this study is to investigate using Structural Equation Modeling(SEM), whether individual creativity of executives of 132 companies with research organizations among domestic semiconductor companies in Korea influences firms’ innovation performance through entrepreneurship orientation and technology innovation orientation. We applied the personal creativity level measurement index, the entrepreneurial orientation measurement factor, and the technology innovation orientation measurement factor identified in the previous research literature |
|
Mohd Noor, N.A. and Aljanabi, A.Q.R.A., 2016. | International Review of Management and Marketing, 6(4), pp.704-710. | The present study purposes to examine the moderating role of absorptive capacity (ACAP) on the relationship between entrepreneurial orientation (EO) and technological innovation capabilities (TIC) among small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in the construction industry. Due to the critical role of SMEs in the construction industry, this article aims to examine to what extent the externally generated knowledge manifested in ACAP can strengthen the relationship between EO and TIC.To validate the proposed model, self-administered questionnaire were conducted to gather data from SMEs owners, 249 questionnaires returned and used for statistical analysis out of 278 distributed.The present research outcomes reflect that both ACAP and EO have significant effects on TIC. Furthermore, the results indicate the moderating role of ACAP on the nexus between EO and TIC. |
|
Audretsch, D., 2012. | Management decision. | With the rapid emergence of scholarly thinking and analysis about entrepreneurship has come a multiplicity of approaches, emanating from different academic traditions. This has resulted in an academic field that is complex and heterogeneous with respect to approaches, methodologies and even the understanding about what exactly constitutes entrepreneurship. The purpose of this paper is to try to reconcile the different approaches and views about entrepreneurship that are prevalent in the literature. |
|
Nambisan, S., 2017. | Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 41(6), pp.1029-1055. | New digital technologies have transformed the nature of uncertainty inherent in entrepreneurial processes and outcomes as well as the ways of dealing with such uncertainty. This has raised important questions at the intersection of digital technologies and entrepreneurship—on digital entrepreneurship. We consider two broad implications—less bounded entrepreneurial processes and outcomes and less predefined locus of entrepreneurial agency—and advance a research agenda that calls for the explicit theorizing of concepts related to digital technologies. In articulating the promise and value of such a digital technology perspective, we consider how it would build on and enrich existing entrepreneurship theories. |
|
Kogan, L., Papanikolaou, D., Seru, A. and Stoffman, N., 2017. | The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 132(2), pp.665-712. | We propose a new measure of the economic importance of each innovation. Our measure uses newly collected data on patents issued to U.S. firms in the 1926 to 2010 period, combined with the stock market response to news about patents. Our patent-level estimates of private economic value are positively related to the scientific value of these patents, as measured by the number of citations the patent receives in the future. Our new measure is associated with substantial growth, reallocation, and creative destruction, consistent with the predictions of Schumpeterian growth models. Aggregating our measure suggests that technological innovation accounts for significant medium-run fluctuations in aggregate economic growth and TFP. Our measure contains additional information relative to citation-weighted patent counts; the relation between our measure and firm growth is considerably stronger. Importantly, the degree of creative destruction that is associated with our measure is higher than previous estimates, confirming that it is a useful proxy for the private valuation of patents. |
|
Smith, C. and Mackinnon, M., 2019. | Journal of Education (University of KwaZulu-Natal), (77), pp.115-137. | After the national transition in 1994, South Africa was welcomed back into the international political and economic arena. Becoming part of the global community, including emerging economies, has had major implications for the country, including its school system. The previously relatively stable, predictable, if unjust, school system needed radical change. In this paper, we report on how Organisation Development (OD) as an action research school change strategy was introduced to a school staff. The outcome has been a gradual change in the organization culture of the school. This includes more collaborative decision-making, open communication, teacher leadership, increased enthusiasm among teachers, and an on-going process of incremental school change. We suggest that OD is a feasible change strategy for schools and school systems in emerging contexts of rapid and ongoing change in which schools are expected to take increasing responsibility for themselves. |
|
Su, Z., Ahlstrom, D., Li, J. and Cheng, D., 2013. | R&D Management, 43(5), pp.473-485. | This study focuses on the impact of knowledge creation capability and absorptive capacity on product innovativeness. Capabilities contribute through their uniqueness, integration into effective configurations, and deployment in response to external environment changes. Therefore, this study examines the individual (uniqueness) and interactive (integration) effects of knowledge creation capability and absorptive capacity on product innovativeness as well as how these effects vary in differing technologically turbulent contexts (deployment). Based on a survey of 212 C hinese firms, this study finds that in addition to their individually positive effects, knowledge creation capability and absorptive capacity synergistically affect product innovativeness. Moreover, the individual effect of knowledge creation capability and the synergistic effect become stronger as technological turbulence increases, whereas the impact of absorptive capacity tends to be dampened by technological turbulence |
|
Baden-Fuller, C. and Haefliger, S., 2013. | Long range planning, 46(6), pp.419-426. | Business models are fundamentally linked with technological innovation, yet the business model construct is essentially separable from technology. We define the business model as a system that solves the problem of identifying who is (or are) the customer(s), engaging with their needs, delivering satisfaction, and monetizing the value. The framework depicts the business model system as a model containing cause and effect relationships and provides a basis for classification. We formulate the business model relationship with technology in a two-way manner. First, business models mediate the link between technology and firm performance. Secondly, developing the right technology is a matter of a business model decision regarding openness and user engagement. We suggest research questions for technology management, innovation, and strategy. |
|
Lee, V.H., Leong, L.Y., Hew, T.S. and Ooi, K.B., 2013 | Journal of knowledge management. | This paper purports to analyze the relationship between knowledge management (KM) and technological innovation in the Malaysian manufacturing sector. Furthermore, the interrelationships between the KM dimensions will also be investigated. Survey data from 162 manufacturing firms were obtained. Multiple linear regression and neural network analysis were performed in this study to examine the relationships between KM and technological innovation; as well as the interrelationships between KM practices themselves. |
|
Zahra, S.A. and Wright, M., 2016. | Journal of Management Studies, 53(4), pp.610-629 | There is a need to rethink and redefine the social value added of entrepreneurial activities to society. In this paper we develop five pillars on which the evolving social role of entrepreneurship can rest and have its impact: (1) connecting entrepreneurial activities to other societal efforts aimed at improving the quality of life, achieving progress, and enriching human existence, (2) identifying ways to reduce the dysfunctional effects of entrepreneurial activities on stakeholders, (3) redefining the scope of entrepreneurial activities as a scholarly arena, (4) recognizing entrepreneurship’s social multiplier, and (5) pursuing blended value at the organizational level, centring on balancing the creation of financial, social and environmental wealth. In a final section we discuss implications for practices and for further research. |
|
Block, J.H., Thurik, R. and Zhou, H., 2013. | Journal of Evolutionary Economics, 23(4), pp.693-718. | The knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship seeks to explain the fundamentals and consequences of entrepreneurship with respect to economic performance. This paper uses the knowledge spillover theory to explain different innovation outcomes. We hypothesize that a high rate of entrepreneurship facilitates the process of turning knowledge into new-to-the-market innovation but has no effect on the relationship between knowledge and new-to-the-firm innovation. Our results using European country-level and pooled OLS, fixed- and random-effects regressions show that a high rate of entrepreneurship increases the chances that knowledge will become new-to-the-market innovation. The findings highlight the importance of Schumpeterian entrepreneurship in the process of the commercialization of knowledge. We discuss the implications for entrepreneurship and innovation policy. |
|
Duobiene, J., 2013. | Economics & Management, 18(3). | The paper deals with the development of corporate entrepreneurship in different stages of organizational life-cycle. The research presents a model for the evaluation of corporate entrepreneurship and systemizes relevant theoretical and empirical research in the field of entrepreneurship and corporate entrepreneurship. Moreover, it describes the development of corporate entrepreneurship in the entire organizational life-cycle since most of researchers who discuss the topics of corporate entrepreneurship and organizational life-cycle, focus on the establishment and growth of organizations. Thus, only some research works analyze corporate entrepreneurship in further stages of organizational life-cycle. The theoretical background of the research is based on Schumpeter’s (1942) approach to entrepreneurship, transformed into organizational level and developed by Pinchot and Pinchot (1994), and Miller and Friesen’s (1984) five stage life-cycle model. The research methodology derives from the quantitative approach that was applied in 77 Lithuanian organizations. The research model and questionnaires are developed and adapted from Wickham’s (2004) model of entrepreneurship by means of updating three characteristics of entrepreneurship, i.e. innovations, strategic objectives and potential for growth, to the relevant and appropriate for quantitative research content of corporate entrepreneurship. |
|
Ashworth, C.J., 2012. | International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 8(2), pp.165-201. | Following calls to explore organizational development in a fashion retail marketing context this paper conceptualizes and explains how 14 fashion retailers operating purely online have developed their enterprises via a six-stage approach, through which they moved at various speeds, either in a linear sequence or concurrently. Effective strategies to secure sustainability for comfort-zone and growth-oriented enterprises are identified, including the development of online portfolios which acknowledges the presence of habitual entrepreneurship in fashion electronic retailing. This paper represents the first in-depth multiple case study into independent, successful pure-players marketing clothing, footwear and accessories categories online. A qualitative case approach is employed from a social constructionist perspective. Rich data is generated via in-depth interviews with owner-managers. Results are developed through thematic qualitative analysis and theoretical contributions are based on data saturation across cases and fashion categories, thus offering strong horizontal and vertical credibility. Findings stress the role of developing internet-technology competencies, strategic marketing and service capabilities in the quest for successful e-retailing in pure-play enterprises, alongside overseas market development and demonstrate an emphasis on planning for the small firm. |
|
Komarova, A., Tsvetkova, L., Kozlovskaya, S. and Pronkin, N., 2019. | Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22(5), pp.1-15. | This article presents problems of application of the corporate Information systems and discloses the need for teaching the corresponding application techniques within the framework of entrepreneurship education. Based on the analysis of insurance companies, this study finds ways to evaluate the level of information systems development within the enterprise. To accomplish the evaluation, we have analyzed the factors influencing the corporate Information systems. The results were obtained on the basis of assessments of nine (9) expert specialists, who have analyzed 5 insurance companies. We have assessed the following factors: level of the innovation potential of an enterprise; degree of utilization of the business analysis instruments at the enterprise; level of interconnections between the corporate information systems and business analysis; the needs of the corporate Information systems in the course of utilization of the business analysis instruments. Analysis has shown that practically all groups are characterized by the worst values, except for the “Finances” group, within which the intensity of utilization of these technologies is moderate. As a result, we have revealed those business instruments that are important for an enterprise and have high significance and efficiency values. |
|
Aarikka-Stenroos, L. and Jaakkola, E., 2012. | Industrial marketing management, 41(1), pp.15-26. | This paper examines the collaborative value co-creation process in the context of knowledge intensive business services. Through 120 qualitative interviews with suppliers and buyers of knowledge intensive services, the extensive exploratory study analyzes the activities, roles and resources of buyers and suppliers in the reciprocal value co-creation process, and their implications for the resulting value-in-use. The paper draws on the literature on value creation, solutions and professional services marketing, and service-dominant logic. It provides a framework depicting value co-creation through a dyadic problem solving process, comprising activities such as diagnosing needs, designing and producing solutions, organizing the process and resources, managing value conflicts, and implementing the solution. The framework serves as a managerial tool to determine critical resources and roles for suppliers and customers, facilitate joint activities, and optimize resource utilization. Insights from this research are broadly applicable to the contexts of knowledge intensive and solutions business. |
|
Durst, S. and Edvardsson, I.R., 2012. | Journal of Knowledge Management. | This paper aims to review research on knowledge management in small and medium‐sized enterprises to identify gaps in the current body of knowledge, which justify future research directions. The study consists of a systematic review of 36‐refereed empirical articles on knowledge management and small and medium‐sized enterprises. The areas of knowledge management implementation, knowledge management perception, and knowledge transfer are relatively well researched topics; whereas knowledge identification, storage/retention and knowledge utilization are poorly understood. Given the prevalence of small and medium‐sized enterprises there is a strong need for more research on this important topic. The future research directions proposed by the authors may help to develop a greater understanding of knowledge management in small and medium‐sized enterprises. |
Azar, G. and Ciabuschi, F., 2017. Organizational innovation, technological innovation, and export performance: The effects of innovation radicalness and extensiveness. International Business Review, 26(2), pp.324-336.
Bjerke, M.B. and Renger, R., 2017. Being smart about writing SMART objectives. Evaluation and program planning, 61, pp.125-127.
Corporate Finance Institute, 2020. SMART Goal – Definition, Guide, And Importance Of Goal Setting. [online] Corporate Finance Institute. Available at: <https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/other/smart-goal/> [Accessed 24 July 2020].
Feki, C. and Mnif, S., 2016. Entrepreneurship, technological innovation, and economic growth: empirical analysis of panel data. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 7(4), pp.984-999.
Jeon, I.O., 2017. The Impact of Entrepreneurship on Corporate Performance: Focusing on the Effects of Technological Innovation and Marketing Competence. Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Venturing and Entrepreneurship, 12(3), pp.87-105.
Mohd Noor, N.A. and Aljanabi, A.Q.R.A., 2016. Moderating role of absorptive capacity between entrepreneurial orientation and technological innovation capabilities. International Review of Management and Marketing, 6(4), pp.704-710.
Ogbeiwi, O., 2017. Why written objectives need to be SMART. British Journal of Healthcare Management, 23(7), pp.324-336.
Shin, J.H., Cho, K.T. and Park, S.H., 2018. The effect of executives’ creativity on firms’ innovative performance: focusing on the mediating effects of entrepreneurial orientation and technological innovation orientation of research organization. Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Venturing and Entrepreneurship, 13(1), pp.73-87.
Zhang, S., Gao, B. and Sun, L., 2018, November. Business Models Innovation and Venture Capital Intention of Technology Entrepreneurship Projects: Inverted U-moderating Role of Technological Innovation. In 2018 International Conference on Economics, Business, Management and Corporate Social Responsibility (EBMCSR 2018). Atlantis Press.
The time required to write a master’s level full dissertation varies, but it typically takes 6-12 months, depending on research complexity and individual pace.